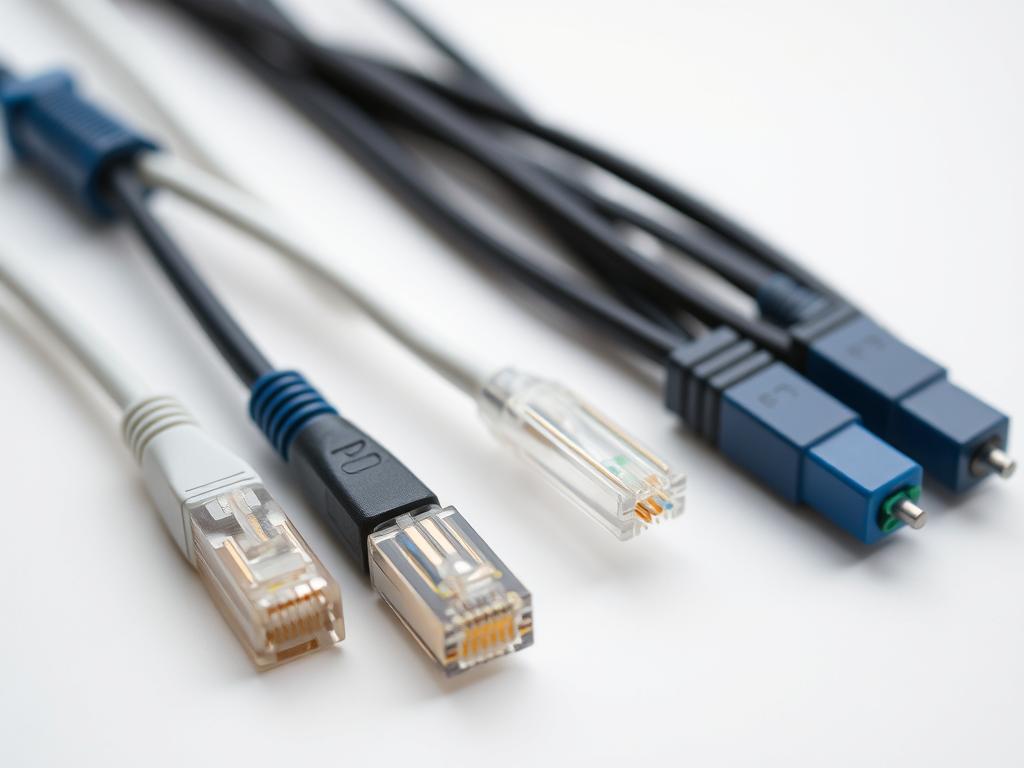
What Is a Network Cable on a Computer? Types & Functions
Network cables are vital for computer networking. They enable smooth data transmission between devices. These cables form the backbone of modern digital communication systems1.
They connect computers, routers, switches, and other network equipment. This allows for quick information exchange across various tech platforms.
Network cables act as communication pathways for digital signals. Twisted pair cabling is the most common type in homes and offices1.
These cables support different data speeds and performance levels. They range from basic connectivity to high-bandwidth applications.
Modern network cables come in various categories. Each is designed for specific performance needs. Some cables support speeds up to 10 Gbps over different distances2.
Cat6 and Cat6a cables offer strong performance for most networking needs. Choosing the right cable depends on bandwidth, environment, and device distance.
Professional networks rely on carefully chosen cables. Proper installation and upkeep can reduce connectivity issues. This enhances overall network performance2.
Network cables are crucial in all settings. They maintain seamless digital communication in homes and large corporate data centres.
Understanding Network Cables: Basic Definition and Purpose
Network cables are vital for modern IT infrastructure. They enable smooth signal transmission and business communications across various sectors3.
These communication conduits connect devices and support data transfer. Network cables come in various configurations to meet specific technological needs4.
Role in Modern IT Infrastructure
Network cables are crucial in today’s digital landscape. They provide pathways for data transmission, supporting small office networks and complex enterprise environments5.
- Enables reliable device connectivity
- Supports high-speed data transfer
- Facilitates seamless business communications
Signal Transmission Basics
Network cables convert digital information into electrical or light signals. Ethernet cables support various transmission speeds depending on their category3:
| Cable Category | Maximum Speed | Bandwidth |
|---|---|---|
| Category 5 | 100 Mbps | 100 MHz |
| Category 6 | 10 Gbps | 250 MHz |
| Category 8 | 40 Gbps | 2 GHz |
Importance in Business Communications
Quality network cabling is essential for efficient business operations. Advanced cable technologies ensure reliable, high-speed communication networks that support critical digital infrastructure4.
Businesses rely on sophisticated network cables to maintain a competitive edge. These cables reduce downtime and support complex communication needs5.
Main Types of Network Cables and Their Applications
Network infrastructure relies on various cable technologies to transmit data effectively. Understanding each cable type helps professionals choose the best solution for specific networking needs.
Coaxial Cables: Legacy and Modern Connections
Coaxial cables have a centre conductor surrounded by a metal shield insulated by plastic. This design blocks external electromagnetic interference6. These cables were key in early networking, with top speeds of 10 Mbps7.
Thick Ethernet (10Base-5) supports cable lengths up to 500 metres. Thin Ethernet (10Base-2) reaches 185 metres7.
Fibre Optic Cables: High-Performance Data Transmission
Fibre optic cables offer top-notch network connectivity for long-distance and high-bandwidth uses. They come in two main types:
- Single-mode fibre (SMF) for extended distance transmission
- Multi-mode fibre (MMF) for high-data-capacity scenarios
These advanced cables can support data rates up to 400 Gbps. Ongoing research explores even higher transmission speeds7.
Twisted Pair Cables: Versatile Networking Solutions
Twisted pair cables are common in modern network setups. They come in two main types:
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP): Ideal for high-interference environments6
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP): Cost-effective and widely deployed6
Different cable categories offer varying performance levels. Cat5e supports speeds up to 1 Gbps. Cat6 and Cat7 provide better capabilities for demanding network setups7.
Patch Cables: Connecting Network Components
Patch cables are vital for short-distance connections in network closets and data centres. These special cables allow precise and efficient links between networking gear.

Network Cable Categories and Performance Standards
Network cable categories shape Ethernet standards. They define network performance across different technological generations8. These categories span from Cat1 to Cat8, each marking significant advancements in data transmission9.
Cable categories show remarkable improvements in network capabilities:
- Cat3 supports 10 Mbps transmission speeds at 16 MHz9
- Cat5 enables 100 Mbps speeds at 100 MHz9
- Cat6A delivers 10 Gbps speeds at 500 MHz9
- Cat8 supports up to 40 Gbps at 2 GHz9
Grasping these categories helps pros choose the right infrastructure. Modern networks need higher-category cables to meet growing bandwidth demands8.
| Cable Category | Max Speed | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Cat5e | 1 Gbps | 100 MHz |
| Cat6 | 10 Gbps | 250 MHz |
| Cat6A | 10 Gbps | 500 MHz |
| Cat8 | 40 Gbps | 2 GHz |
Selecting the right cable category ensures optimal network performance and future-proofing infrastructure.
Installation Best Practices and Troubleshooting Network Cables
Effective cable installation is vital for robust network performance. Proper cable management can cut troubleshooting time and boost network efficiency. Structured cabling systems can reduce installation time by up to 25%10.
Experts suggest choosing cable types based on specific environmental needs. Shielded cables are crucial in areas with high electromagnetic interference. They can improve network performance by up to 50%10.
Cable selection should consider signal transmission distance and potential interference. Future bandwidth demands are also important factors11.
Regular maintenance is key for network reliability. Certification by qualified technicians can reduce network downtime by up to 30%10. Cable testing and proper labelling are essential practices.
Avoiding sharp bends helps prevent signal degradation and extends cable lifespan12. Organisations with strict cable management can see up to 40% increase in overall productivity10.
FAQ
What exactly is a network cable?
Network cables are physical mediums that enable data transmission between computer devices. They form the backbone of IT systems, connecting networks and facilitating communication. These cables carry electrical or optical signals for data transfer between various network equipment.
What are the primary types of network cables?
The main types include coaxial, fibre optic, and twisted pair cables. Patch cables are also common. Each type suits different networking environments and data transmission needs.
How do network cable categories differ?
Network cable categories range from Cat1 to Cat8. Each category offers improved data speeds, higher frequencies, and better performance. Modern networks typically use Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a cables.
Why is cable quality important in networking?
Cable quality directly impacts network reliability, speed, and overall system performance. High-quality cables reduce signal interference and minimise data loss. They support robust communication, crucial for businesses relying on fast data transfer.
What factors should I consider when installing network cables?
Consider proper cable routing and avoid electromagnetic interference sources. Maintain appropriate cable lengths and follow industry installation standards. Select the right cable type for your networking environment and performance needs.
How often should network cables be replaced?
Inspect network cables regularly and replace them every 5-7 years. Replace sooner if you notice performance issues. Upgrades may be needed due to damage, tech advancements, or changes in network needs.
What are the advantages of fibre optic cables?
Fibre optic cables offer superior bandwidth and longer transmission distances. They’re immune to electromagnetic interference and provide higher security. These cables enable faster data transfer rates than traditional copper-based network cables.
How do twisted pair cables work?
Twisted pair cables have multiple copper wire pairs twisted together. This design reduces electromagnetic interference. They come in shielded (STP) and unshielded (UTP) variants.
UTP is more common in offices and homes. It’s cost-effective and easy to install.
What common issues affect network cable performance?
Common issues include signal degradation, interference, and physical damage. Improper installation, excessive cable length, and wear also impact performance. Regular maintenance, professional installation, and testing can prevent these problems.
Are network cables still relevant with wireless technologies?
Yes, network cables remain crucial despite wireless tech advancements. They provide stable, secure, and high-speed connections. Cables offer lower latency and consistent performance, essential for critical infrastructure and data centres.
Source Links
- Networking cable
- What is a Network Cable? Best Guide for 2024 Insights
- Beginner’s Guide to Network Cables
- The Ultimate Guide to Network Ethernet Cables: Everything You Need to
- Types of Ethernet Cable – GeeksforGeeks
- What Are the 4 Types of Network Cables? – Tevelec
- What are the different types of network cables? | TechTarget
- Ethernet Cables Explained | Eaton
- Ethernet Cable Categories Explained: A Brief History
- Guide to Network Cabling | Expert Network Cabling Installation
- Beginner’s Guide to Network Cables
- What Is Network Cabling & Why Is It Important?